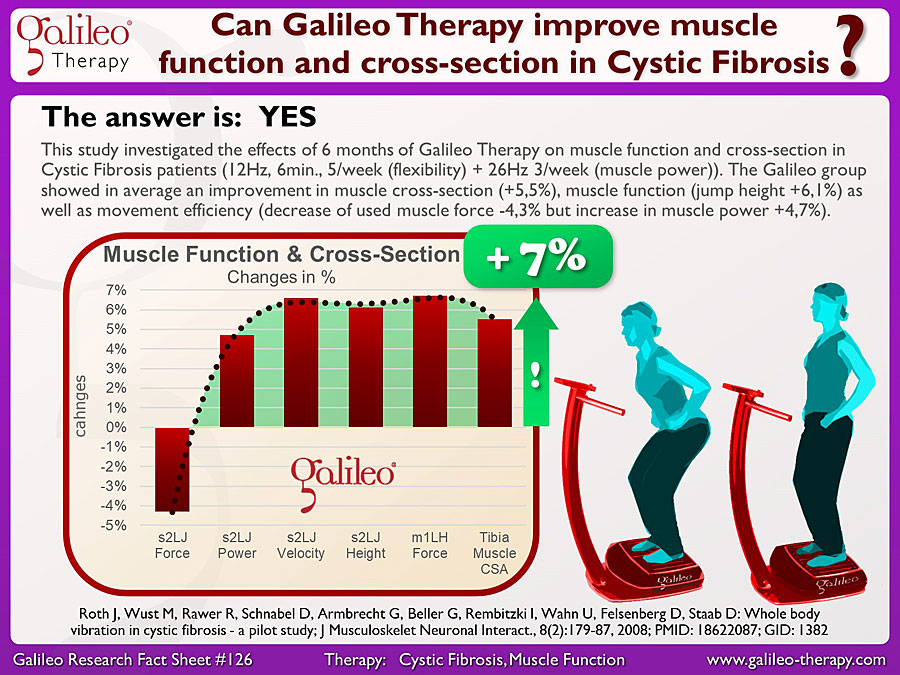
This pilot study documented the effects of 6 months of Galileo Therapy on muscle function and muscle cross-sectional area in Cystic Fibrosis patients. The Galileo Therapy group received 5 times per week Galileo Therapy focusing on flexibility (6 minutes, 12Hz) and 3 times per week focusing on muscle power and muscle mass (6 minutes, up to 26Hz, up to 9kg additional load) – so 48 minutes Galileo Therapy per week altogether. Primary focus was improvement of the flexibility of the very stiff upper body.
The results showed in addition to the already reported improvements in muscle function (#GRFS120an average improvement of the muscle cross-section by 5.5%, an improvement of the maximum voluntary force (m1LH) by +6,7%, in improvement of muscle function (velocity +6,6%, jumping height +6,1%) and an improved movement efficiency at the same time (reduction of the movement specific peak force by -4.2% and increase muscle power (+4,7%) and jumping height (+6,1%) at the same time).
This study is a good example for the fact that a decrease of movement specific peak force (in this case the peak force during lift-off of the counter movement jump) does not need to be a negative effect – in this case the patients got more flexible allowing them a larger degree of counter-movement, therefore a longer counter-movement phase which enabled them to decrease the used force but increase the main movement outcomes (power, velocity, jumping height) and therefore allowing a much more efficient moment pattern.
#GRFS126 #GalileoTherapy #CysticFibrosis #MuscleCrossSection #MuslePower #MuscleForce #s2LJ #m1LH #MechanoStimulation #QualityOfLife #MovementQuality
The verdict of our customers: Excellent
4.7 out of 5 stars based on 868 reviews
Since 1996 we support our Galileo® customers worldwide.
Development and production exclusively in Germany.
10-year service guarantee &
5 year warranty for private customers in Germany
Unlimited user support for all Galileo customers.
Efficacy proven by over 500 scientific publications.
Winter vacation
Dear customers,
Our colleagues have been working for you and your wishes all year – now we’re giving them a well-deserved break. From 24.12.2025 to 6.1.2026, we’re swapping phones for Christmas movies and to-do lists for plates of cookies.
However, our contact form remains as vigilant as a Christmas angel – feel free to write to us and we will get back to you on January 7, 2026, when we are back, refreshed and full of energy!
Merry Christmas and a magical new year
Your Galileo Team
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Vimeo. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information